Introduction
For many aspiring pilots, the goal begins from your first license. But a clear picture of what a First Officer (co‑pilot) actually does is often missing. This role is more than just a junior seat—it’s a critical cornerstone of flight operations and crew safety.
In this article, designed for students pursuing CPL or cadet programs, we’ll break down:
- Key duties of a First Officer
- Co-pilot vs Captain distinctions
- How Marigold Aviation’s preparation equips cadets for this transition
Who Is the First Officer?
The First Officer, also known as the co-pilot, sits on the right seat and serves as the Captain’s second-in-command. In case the Captain becomes incapacitated, the First Officer takes command—legally and operationally.
First Officer Responsibilities
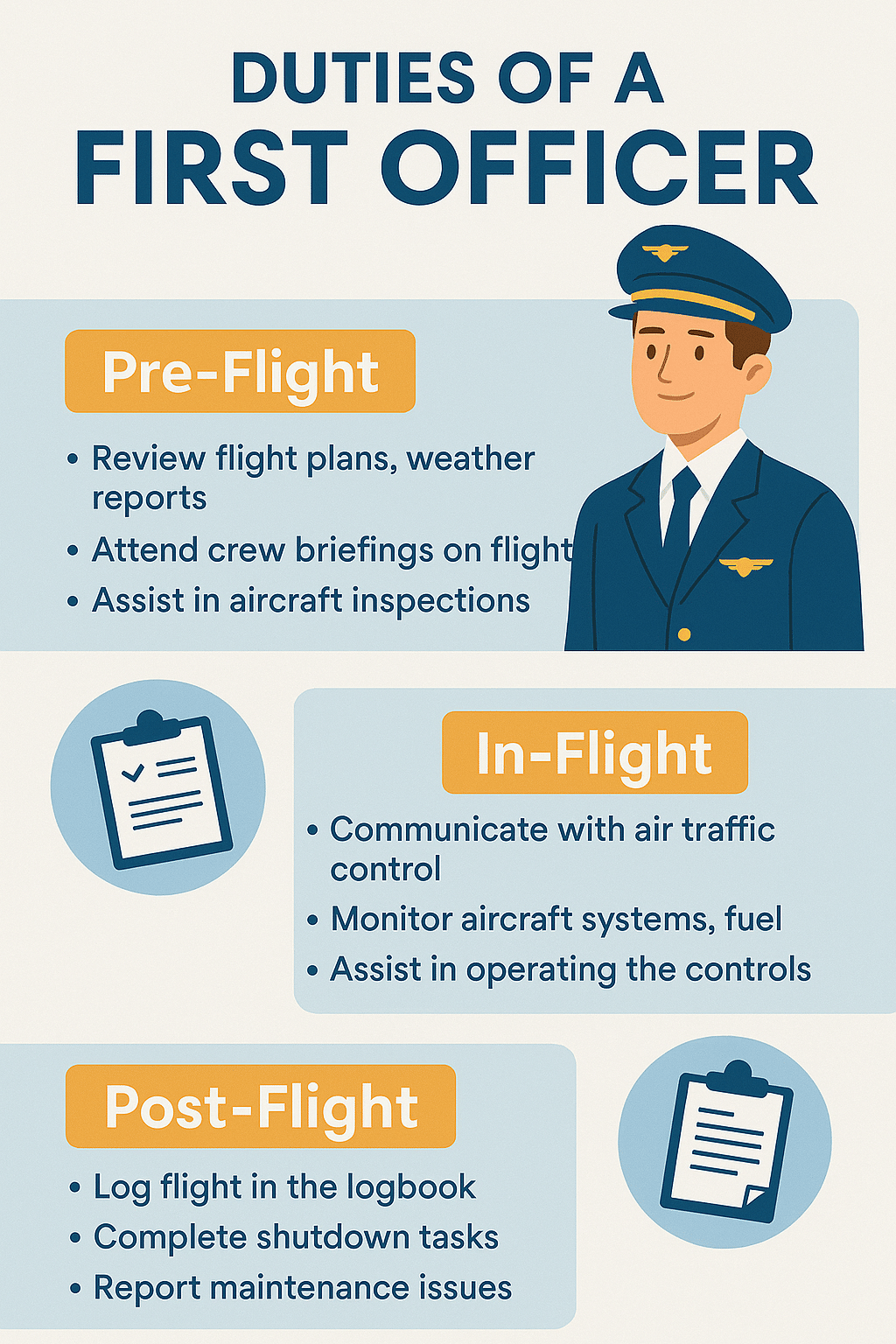
1. Pre‑Flight Planning & Inspection
- Review flight plan, weather, NOTAMs, weight & balance
- Conduct exterior and cockpit inspections to ensure airworthiness
2. Pilot Flying & Pilot Monitoring
First Officers and Captains alternate roles as Pilot Flying (PF) and Pilot Monitoring (PM). PF handles the controls; PM manages radios, checklists, and cross-checking flight parameters.
3. Communication
- Handle ATC communications throughout the flight
- Liaise with cabin and ground crew for coordination and updates
4. System Monitoring & In-Flight Duties
- Monitor aircraft systems like altimeter, fuel, hydraulics, and navigation
- Detect and cross-check anomalies, assist the Captain during abnormal situations
5. Emergency Procedures
- Assist during emergencies following SOPs
- Take action if Captain is unable to fly
- Participate in training for handling system failures and abnormal situations
6. Documentation and Records
- Maintain accurate flight logs, performance sheets, and technical reports
- Ensure regulatory compliance and accountability after flights
FO vs. Captain: Key Differences
While duties often overlap, the Captain holds ultimate legal and operational responsibility for the flight — even when the FO is flying (CAU). First Officers support, advise, and monitor—the Captain makes final decisions.
Skills and Traits Needed to Succeed as a First Officer
- Situational Awareness
- Strong Communication
- Teamwork and Leadership
- Decision-Making Under Pressure
- Adherence to SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures)
These soft and technical skills are deeply emphasized in high-quality pilot training programs like Marigold Aviation’s IndiGo Cadet Pilot Program, where cadets are trained with airline-standard simulation and CRM (Crew Resource Management) sessions.
Career Path from First Officer to Captain
Most pilots begin their commercial career as First Officers. With adequate flying hours, consistent performance, and further certifications (like an ATPL), they can move up to the Captain’s seat.
Average timeline:
- CPL Holder ➝ First Officer (post-type rating)
- First Officer ➝ Senior First Officer (after 1,500–2,000 hours)
- Senior FO ➝ Captain (after 3,000–4,000 hours and experience)
💡 Curious about what comes next? Read our blog: CPL, PPL, and ATP Licenses Explained
Why It Matters in Training & Cadet Programs
At Marigold Aviation, we focus on:
- Simulator-based PF/PM switching drills
- CRM and crew coordination training
- Step-by-step preparation aligned with DGCA and airline expectations
Many of our cadets graduate ready to enter structured programs, such as the IndiGo Cadet Pilot Program, with confidence in first officer capabilities.
Why Aspiring Pilots Should Care
- Early FO experience helps build flight hours, situational awareness, and cockpit discipline.
- Understanding system operations and emergency handling as a First Officer sets you up for Command later.
- Training as an FO under supervision is a trusted stepping stone to becoming a Captain.
Conclusion
The First Officer is not “just the co-pilot” — they are an essential part of every flight, entrusted with safety, communication, and flying responsibilities. For Indian aviation students, this is the first major step after training and licensing — and the foundation of a long, successful career in the skies.
At Marigold Aviation, we ensure you’re prepared not only for your CPL and Type Rating, but also for the professional mindset and technical readiness expected from every airline First Officer. With expert instruction, airline-standard simulators, and placement support, you’re in good hands.






